
The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". These cookies ensure basic functionalities and security features of the website, anonymously.
#Probability calculator trial#
S/he then clicks the 'Calculate' button, and the resultantīernoulli trial calculation will be automatically computed and displayed.īernoulli trial can be used for any scientific calculations.Necessary cookies are absolutely essential for the website to function properly. When a coin is tossed, there are two possible outcomes: Heads (H) or Tails (T) Also: the probability of the coin landing H is the probability of the coin landing T is. The best we can say is how likely they are to happen, using the idea of probability. To use this calculator, a user simply enters in the n and k values, only with the probability that the event will occur. Many events can't be predicted with total certainty. This 26.13% is success rate that 5 out of 7 freshmen will pass the exam. The binomial coefficient of n=7Īnd k=5 will be 21. Using these numbers, we plug them into the formula. The failure rate then will be 1-.6=.4 or 40%. In this example, n=7, k=5, and the success rate is 60% or. If 7 freshmen take the examm, then what will the probability be that 5 pass. Let's say there is an exam where 60% of students pass. To illustrate bernoulli trial, let's go through an actual example where bernoulli trial would be used. If all of these conditions are met, we can apply bernoulli trial to finding the percent outcome that an event will occur.

For example, if probability P (X 3) corresponds to the precisely. Also shown are the four types of cumulative probabilities. In this case, P (X 3) 0.14, or fourteen percent (14). P (X 3) e-5 53 / 3 Calculate the probability manually or using the Poisson distribution calculator. In other words, the probability of an event occurring must be the same, not different, for each trial. Input the values of and x into the equation above. For example, for eachįlip of a coin, there is always a 50% success rate of getting a heads.
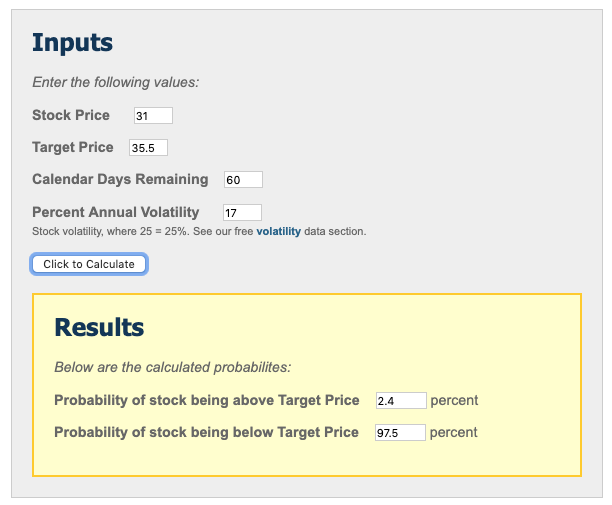
#Probability calculator free#
It represents the failure rate of the event. This is a free online math calculator together with a variety of other free math calculators that compute standard deviation, percentage, fractions, and more. Q n-k represents the probability of the event not occurring. It represents the success rate that the event occurs. P k represents the probability of the event occurring. This means there are 21 different possible combinations weĬan arrange 5 items when taken from a total of 7 items. For example, if we haveĪ total of 7 items and we want to choose 5 items from those 7, then n=7 and k-5, and the binomial coefficient would be equal to 21. The binomial coefficient represents the total different number of combinations we can take k items from a total of n selections. The bernoulli trial is calculated by multiplying the binomial coefficient with the probability of success to the k power multiplied by the probability of failure to the n-k power. The formula for calculating the result of bernoulli trial is shown below: This Bernoulli Trial Calculator calculates the probability of an event occurring.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
